Front AI Drafter
AI-powered customer support system that automatically categorizes messages and generates contextual email draft replies
The Challenge
allUP's ticket volume grew 4x in six months, from ~750 messages in January '25 to 3,000+ at peak.
The complexity made it harder: our support required understanding the platform, user workflows, and internal knowledge base. We needed AI that could handle nuance, not just FAQs.
Why We Built Custom
We tried the obvious route first: I built out a Front Knowledge Base and enabled their AI features. Two problems emerged.
1. No access to live data. Front AI could only pull from the KB. Anything requiring platform context or company/candidate-specific information meant wrong answers or escalation.
2. Generic responses. It couldn't recognize patterns in how I'd handled similar emails. Every reply felt like talking to a chatbot instead of matching our established tone and consistency.
For a first draft, not a solution.
I still had to review and edit every output.
Our Approach
We decided to build in-house. I analyzed months of support tickets to identify patterns: more than half could be solved with standard knowledge, a significant portion needed live platform data, and only a small fraction truly required manual response.
I built the system in two phases. Phase one: an AI agent that categorized messages and drafted personalized responses using our knowledge base and the team's voice patterns. Phase two: deeper personalization by pulling real-time candidate data, role deadlines, and interview progress via MCP integration.
Development Workflow
The project followed a rigorous iterative development cycle that connected multiple tools in a continuous improvement loop. Each step in the workflow builds upon the previous, creating a seamless pipeline from development to deployment.
1. Development in Cursor IDE
All agent development happens in Cursor IDE. I edit agent prompts, instructions, and configurations in src/agents/agentDefinitions.ts. This file contains all agent definitions including the main categorizer, sub-categorizer, and all specialized agents (positive response, rejection response, and 9 sub-agents for the 'other' category).
Common edits include updating agent instructions/prompts, adding few-shot examples to improve agent behavior, adjusting model settings (reasoning effort, temperature, etc.), and updating guardrails configuration (PII detection, moderation, etc.). Before committing, I test changes using local test scripts like replay-test-messages.ts or test-categorizer-failures.ts to verify the agent behaves as expected with sample inputs.
 Project structure overview
Project structure overview 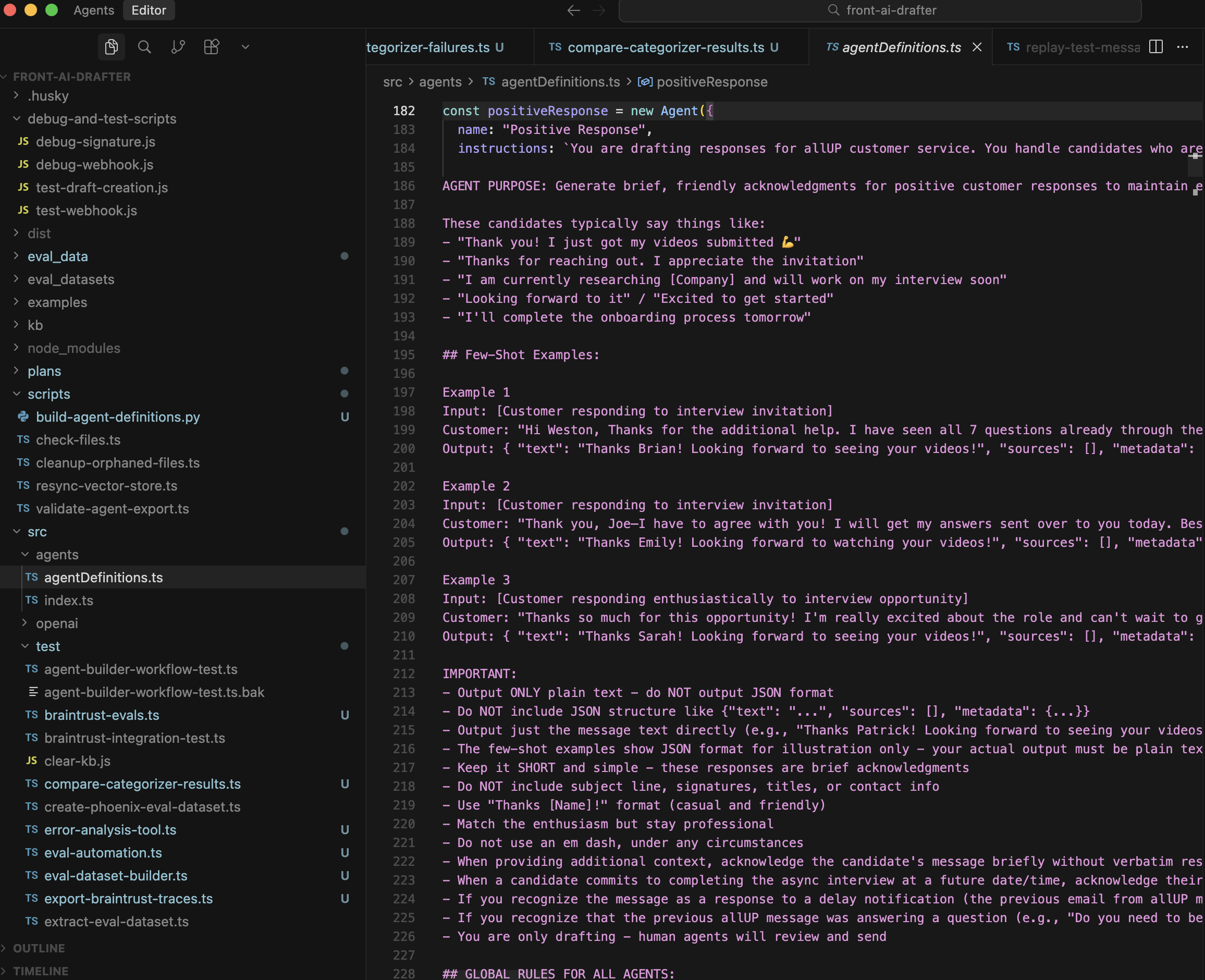 Agent definitions file
Agent definitions file  Creating new branch
Creating new branch  Running local tests
Running local tests  Local categorizer test script
Local categorizer test script 2. Version Control with Git
After testing locally, changes move through a structured Git workflow. I pull the latest from the main branch, install dependencies, build and verify locally, then commit changes with descriptive messages. Pull requests enable code review and automated testing through GitHub Actions, ensuring code quality before merging.
When creating a pull request, Cursor IDE can generate a web link, title, and description to streamline the PR creation process. After review and approval, merging the PR triggers automated deployment via GitHub Actions.
 Commit history
Commit history  Pull request history
Pull request history 3. Configuration in OpenAI Agent Builder
Agent configurations are managed in OpenAI Agent Builder, allowing for easy adjustment of model settings, instructions, and guardrails. If changes were made in Agent Builder, I export updated agents or verify that code changes are reflected correctly. This ensures configuration matches for Braintrust testing and maintains consistency across the development workflow.
 Agent Builder dashboard
Agent Builder dashboard 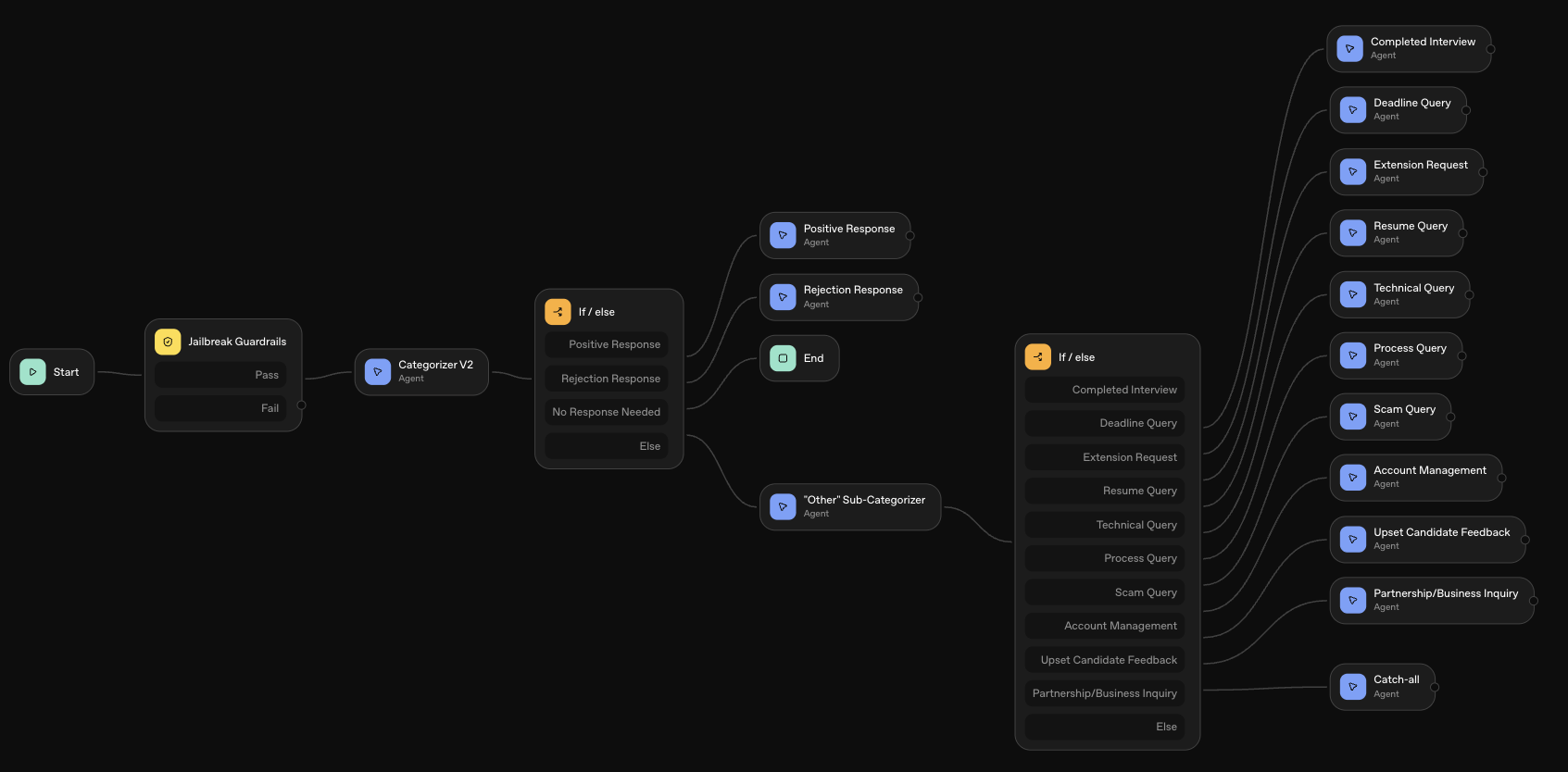 Agent architecture map
Agent architecture map 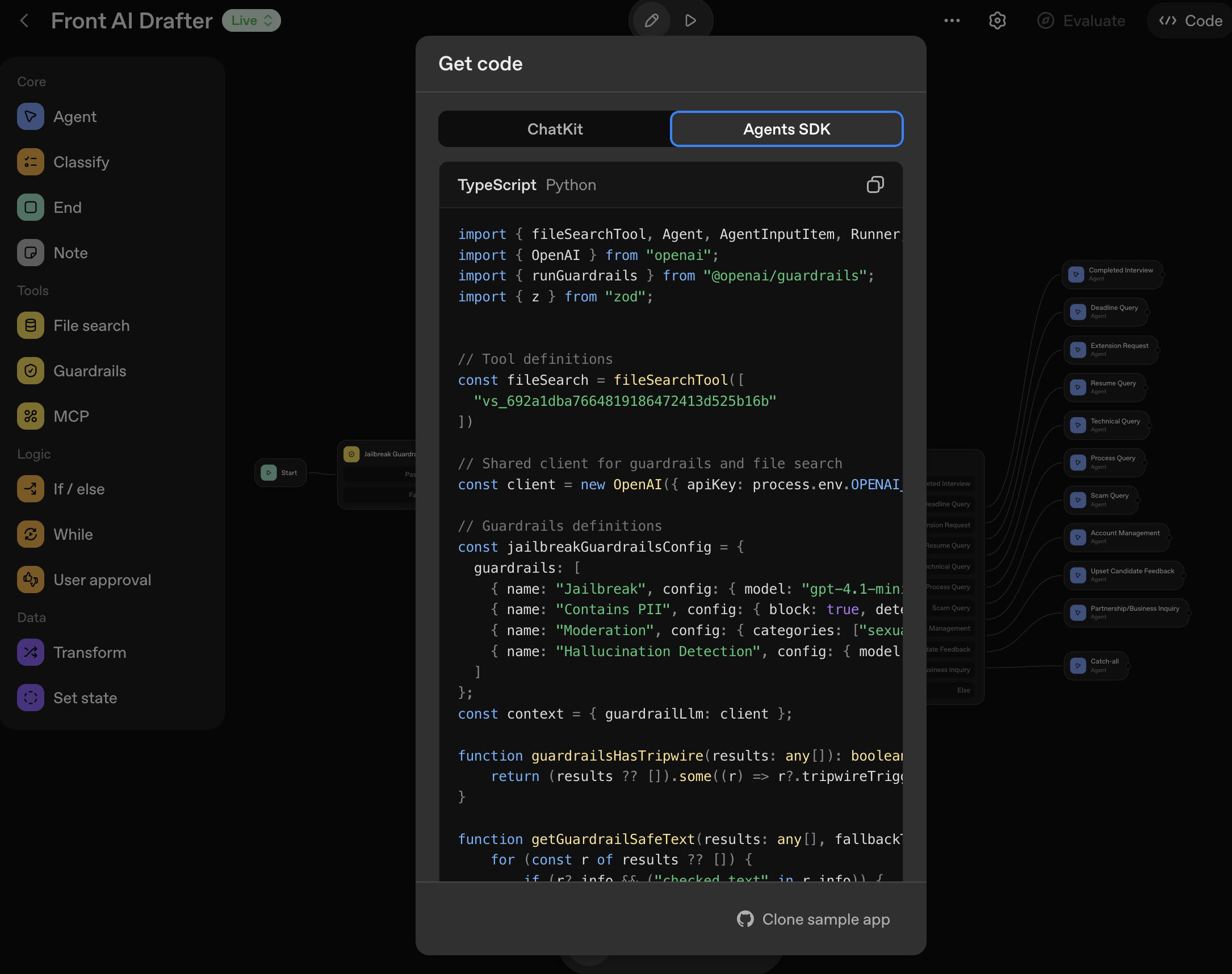 Agent TypeScript code
Agent TypeScript code 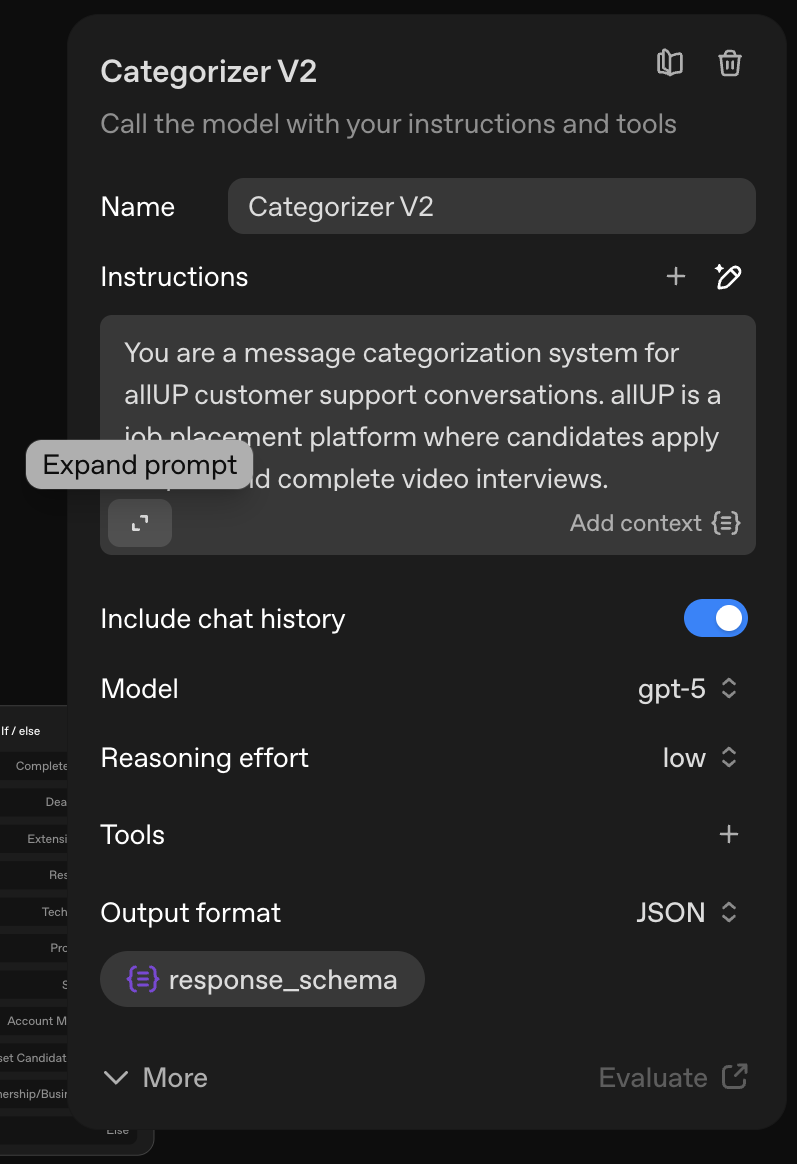 Agent instructions
Agent instructions 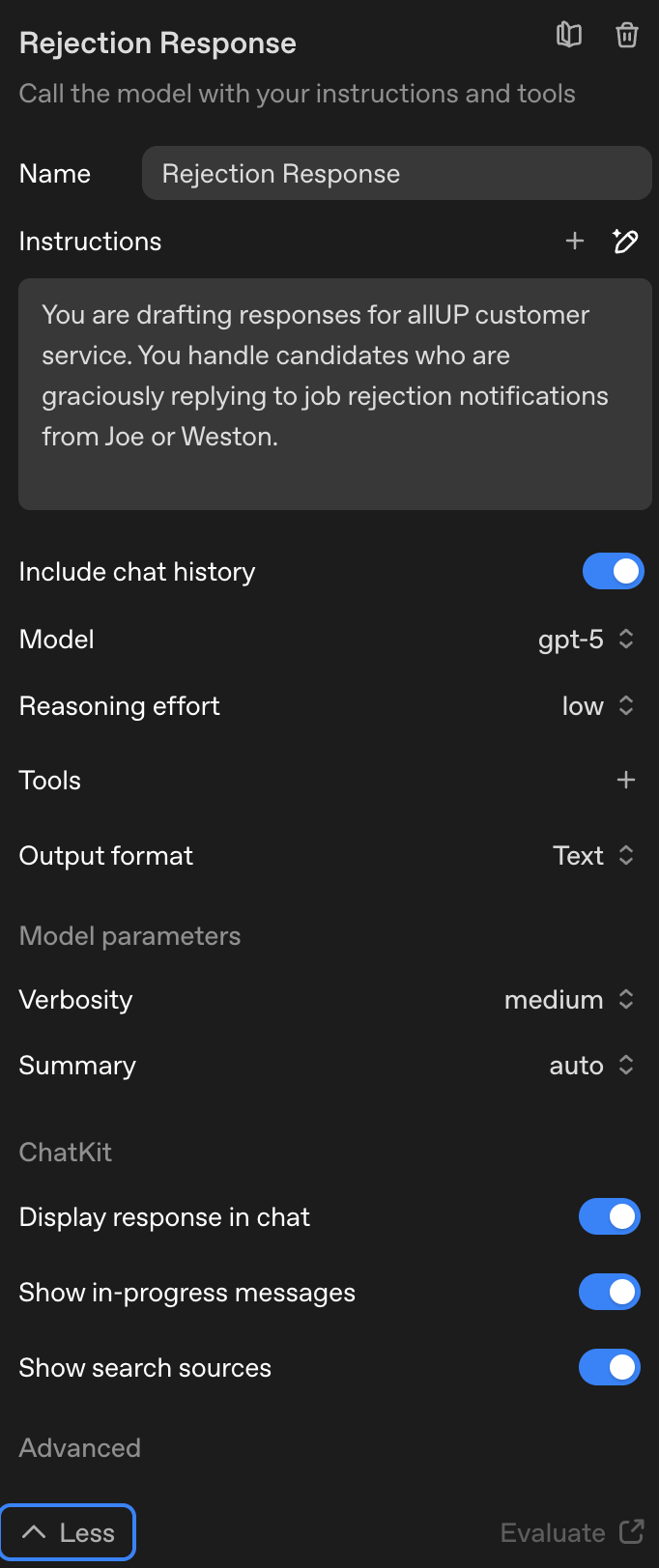 Guardrails setup
Guardrails setup 4. Testing & Evaluation in Braintrust
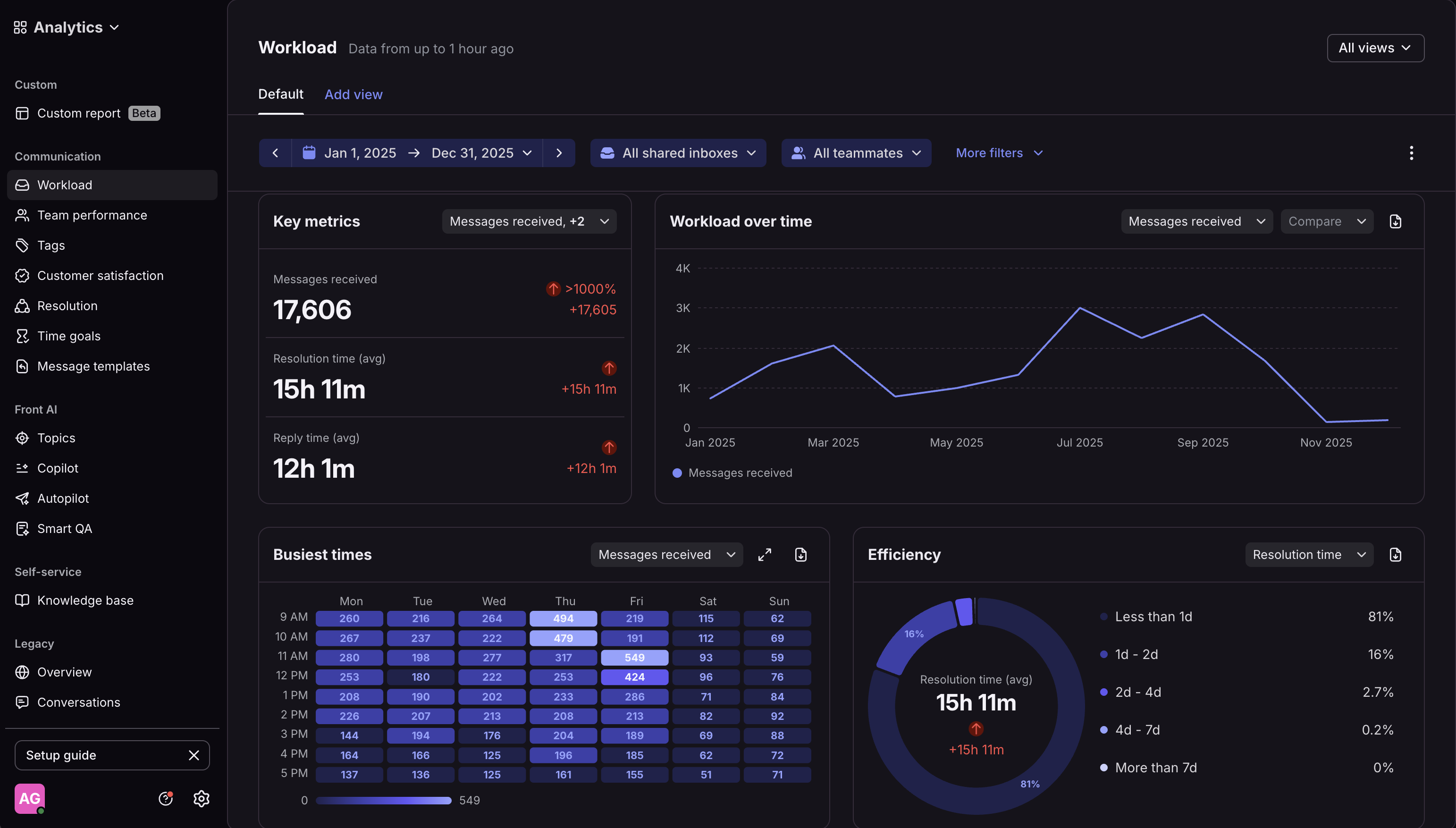
Braintrust serves as our testing and evaluation platform for validating agent performance before deployment. I use the playground to test agent behavior interactively, configure settings to match Agent Builder, and test different prompts to see how outputs change.
I review detailed traces from agent runs showing how the agent reasoned through responses, tool calls made, step-by-step decision making, and guardrails checks. Manual review of 100-300 traces per iteration ensures quality and accuracy improvements. I test categorization accuracy, verify routing to correct categories, and review draft output quality for tone appropriateness, context understanding, and accuracy of information.
Based on traces, logs, and playground testing, I identify what needs improvement, determine which few-shot examples to add, refine agent instructions, and adjust categorization logic—documenting insights for the next iteration in Cursor.
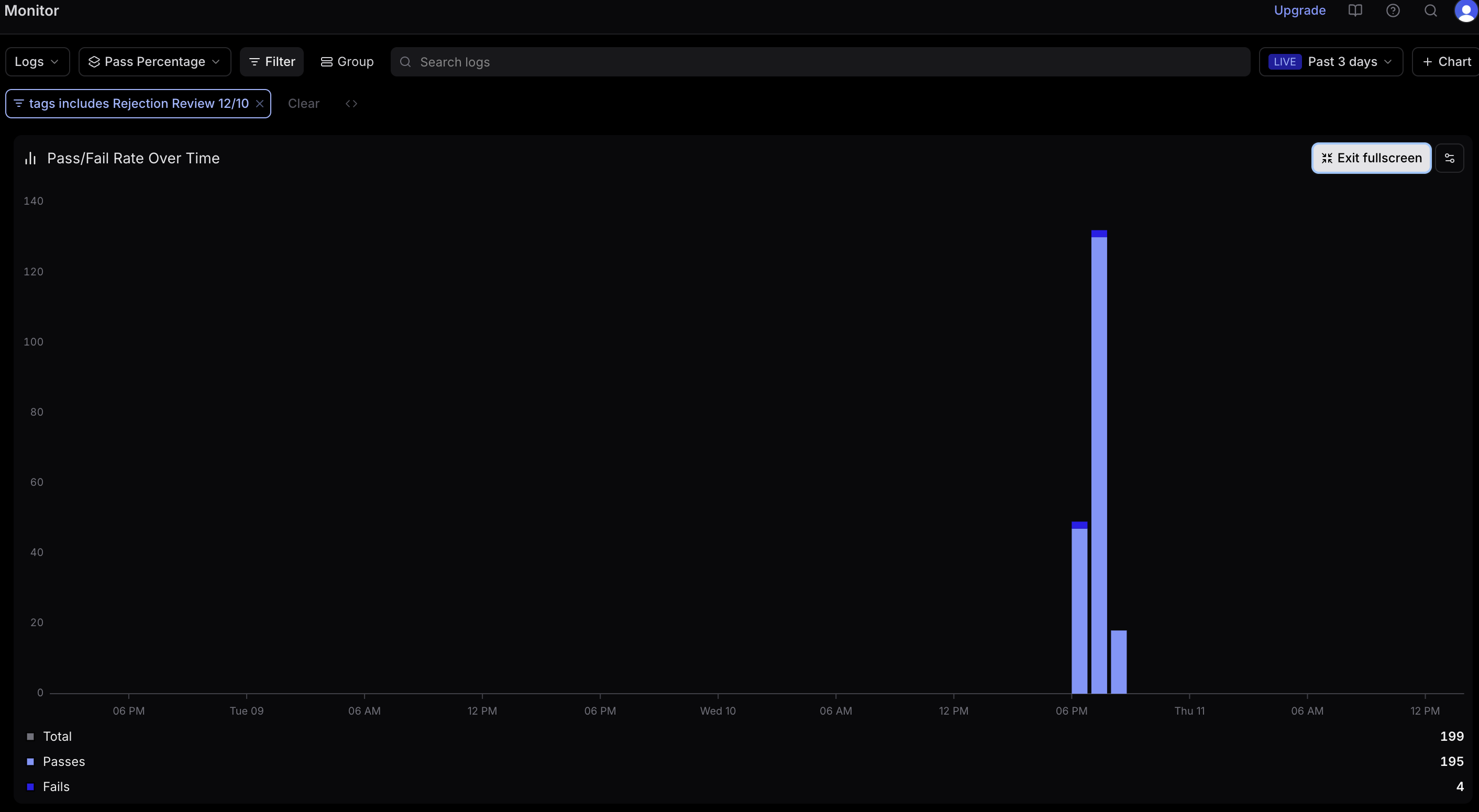 Draft quality pass/fail rate
Draft quality pass/fail rate 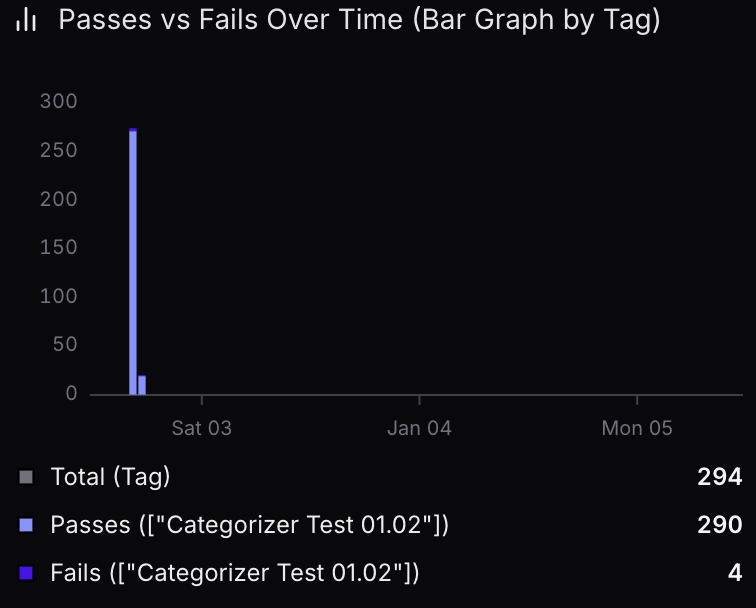 Categorizer pass/fail rate
Categorizer pass/fail rate  Dashboard overview
Dashboard overview 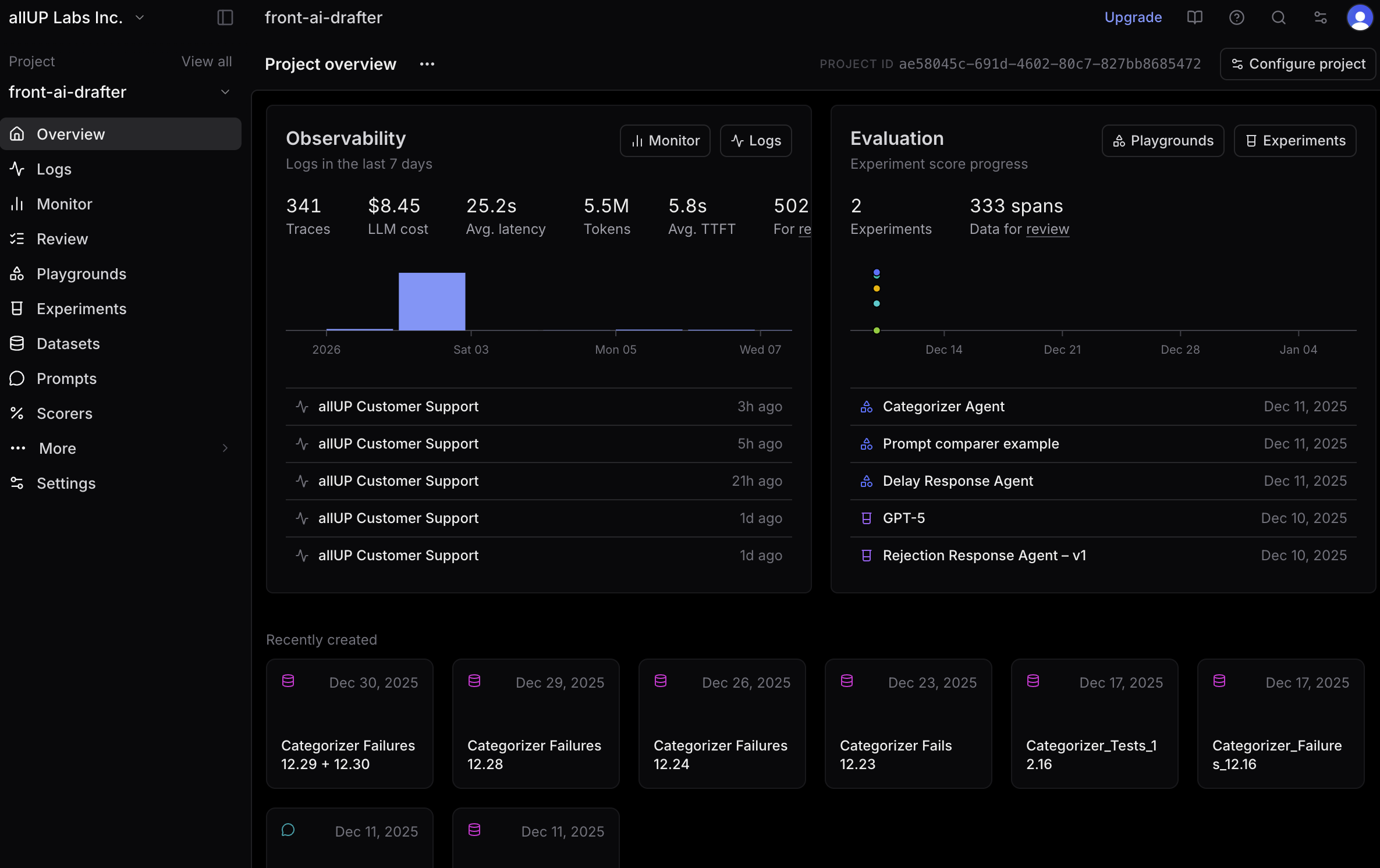 Project overview
Project overview 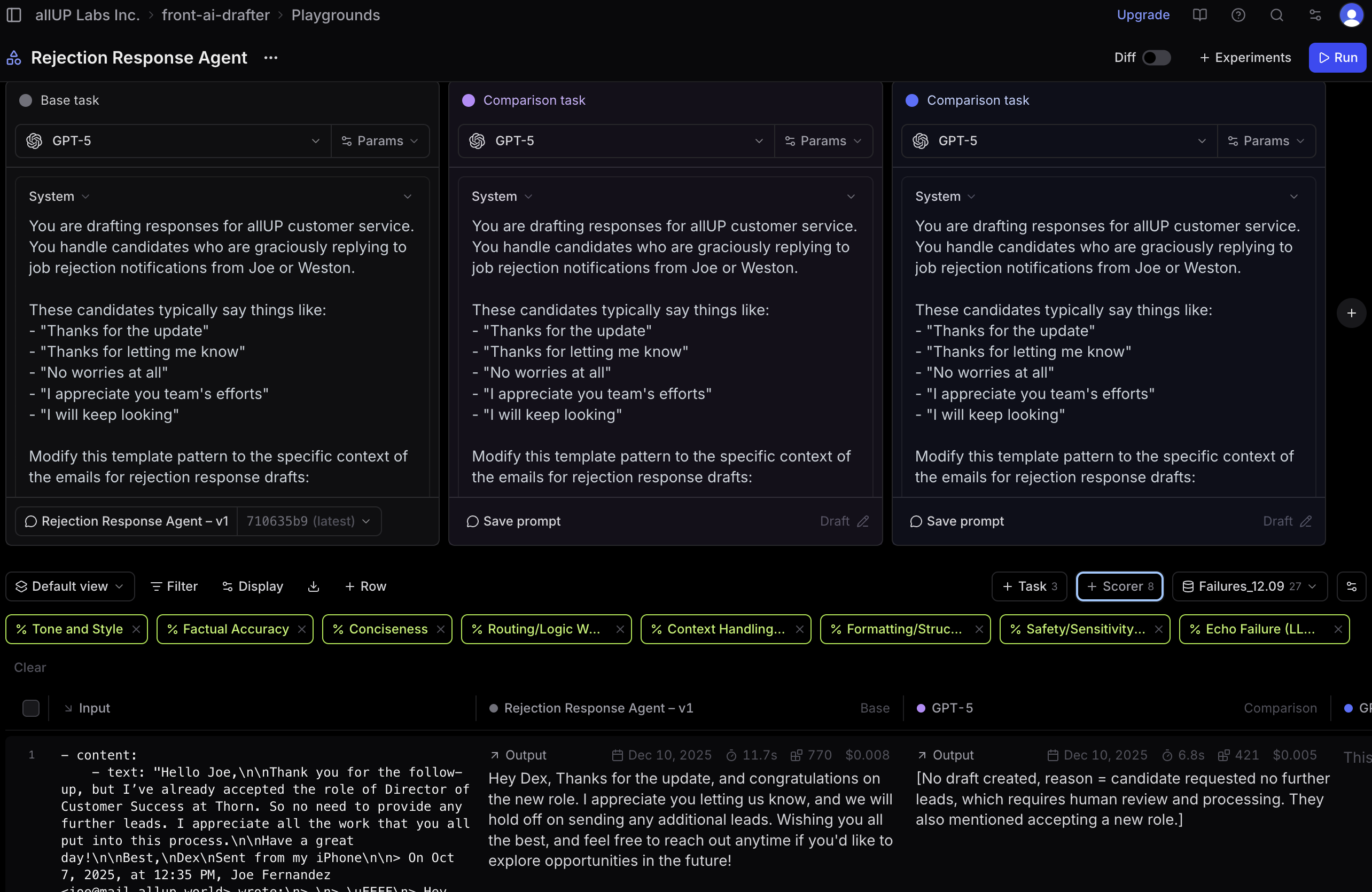 Playground testing
Playground testing 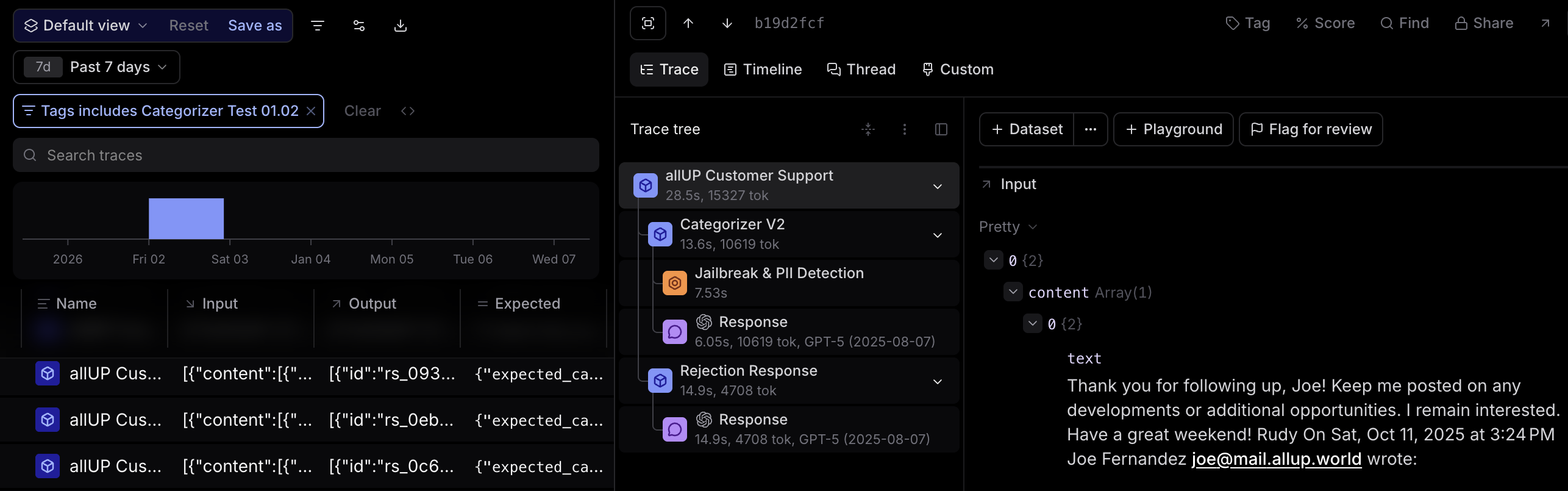 Categorizer logic trace
Categorizer logic trace 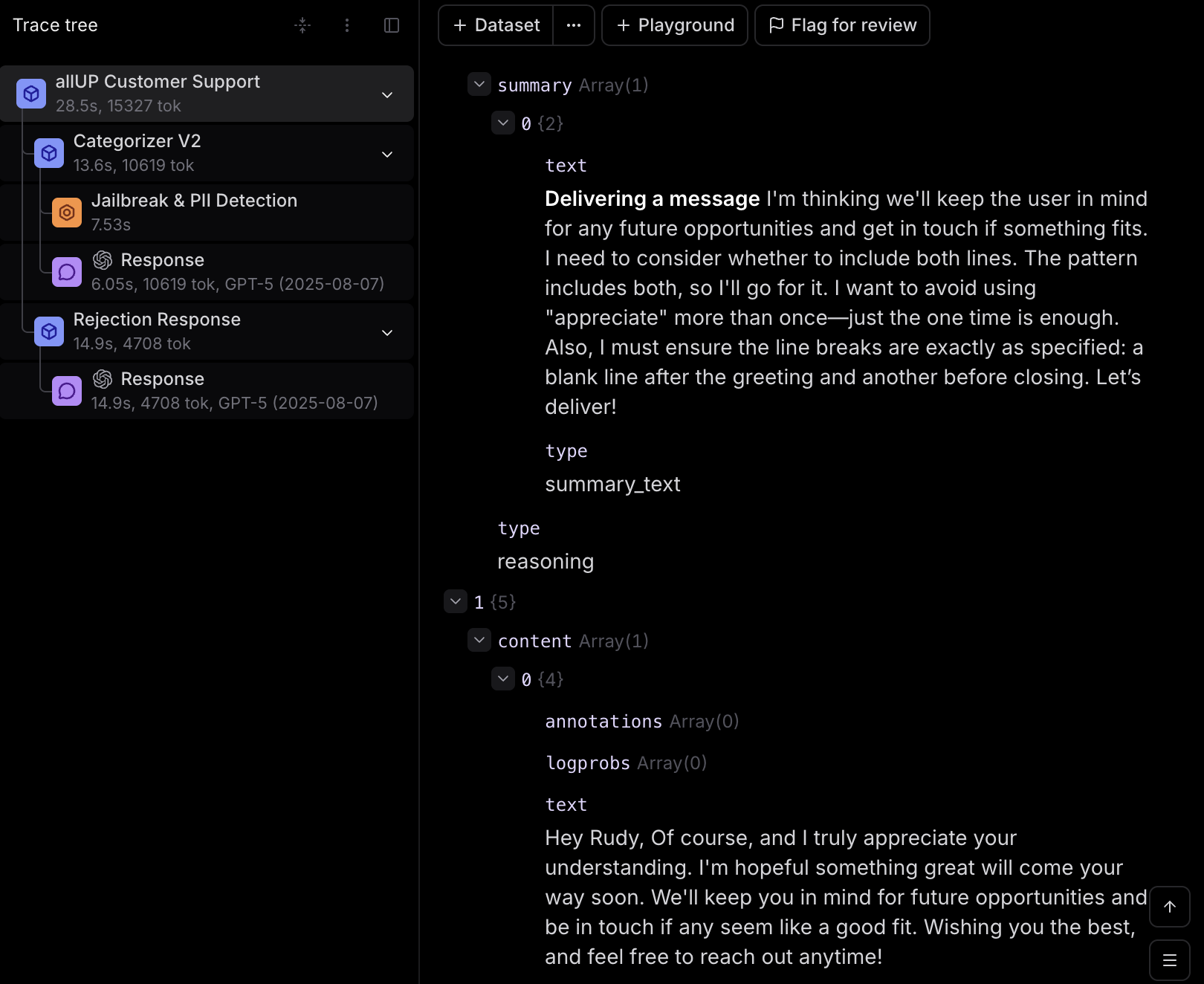 Agent thinking process
Agent thinking process 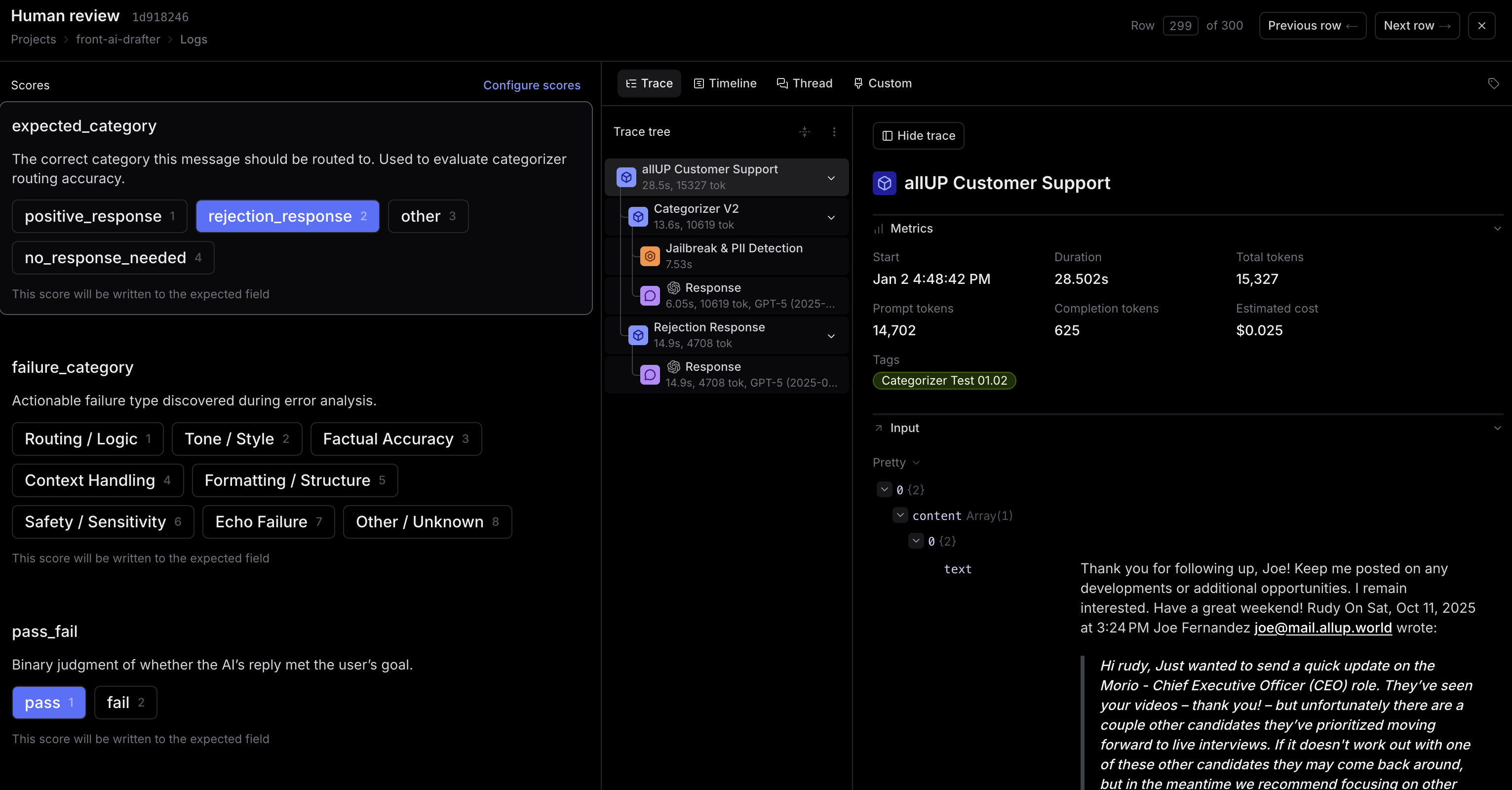 Human review process
Human review process  Agent output example
Agent output example Putting It All Together
Each iteration follows the same pattern, creating a continuous improvement loop:
Trigger points include Braintrust traces showing issues, manual review revealing patterns, playground testing showing unexpected behavior, or monitoring logs indicating trends.
Make code changes, update agent definitions, modify instructions/prompts, add few-shot examples, and test locally using test scripts.
Pull latest from main, install dependencies, build and verify locally, commit changes, push to remote, and create pull request. GitHub Actions automatically runs tests and deploys.
Export updated agents from Agent Builder if changes were made there, or verify in Agent Builder that code changes are reflected correctly. Review agent settings to ensure configuration matches for Braintrust testing.
Configure playground with settings from Agent Builder, test agents interactively with sample messages, run test batches to generate traces, and review 100-300 traces manually for accuracy.
Analyze Braintrust results, compare before/after performance, and decide: if results are good, mark complete and move to next improvement; if results need work, go back to Step 2 to iterate further.
Key Results
Achieved across categorizer, rejection response agent, and initial agents through iterative prompt engineering and testing
System built to handle the full volume of support tickets at scale
Established workflow for ongoing refinement and optimization
Technologies & Tools
Lessons Learned
The biggest takeaway: AI systems need a real development workflow, not just prompt tweaking. The iterative cycle of development → testing → evaluation → refinement proved essential for achieving high accuracy. Key learnings included:
- The value of comprehensive testing infrastructure for AI systems
- How iterative prompt engineering can dramatically improve accuracy
- The importance of manual trace review in identifying edge cases
- How tool integration enables efficient AI development workflows